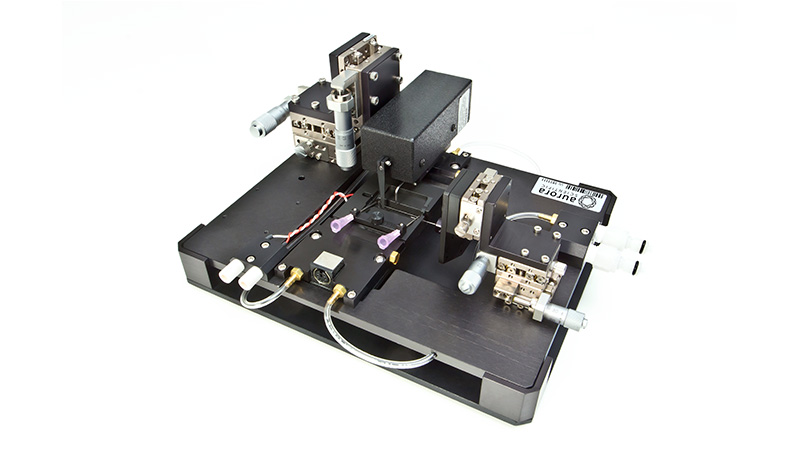
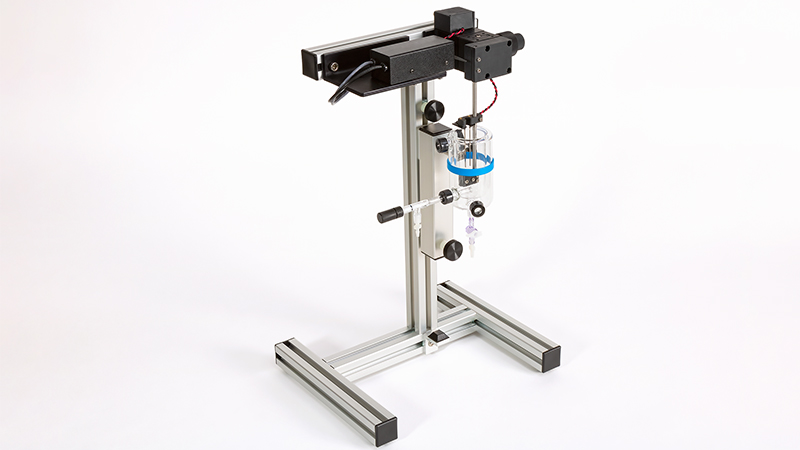
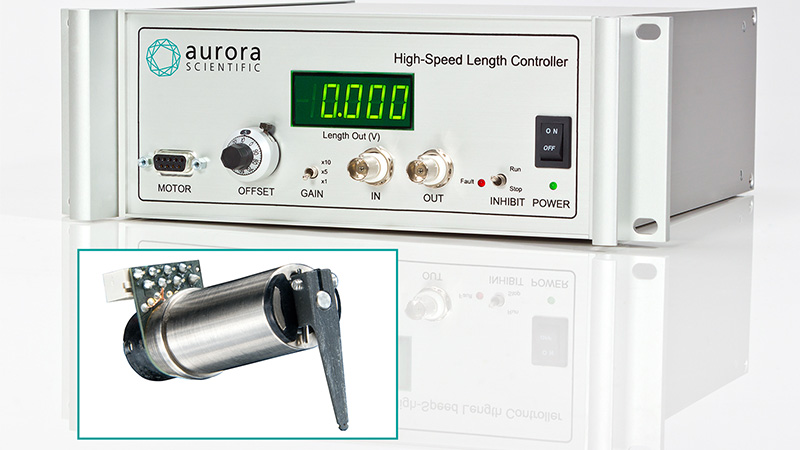
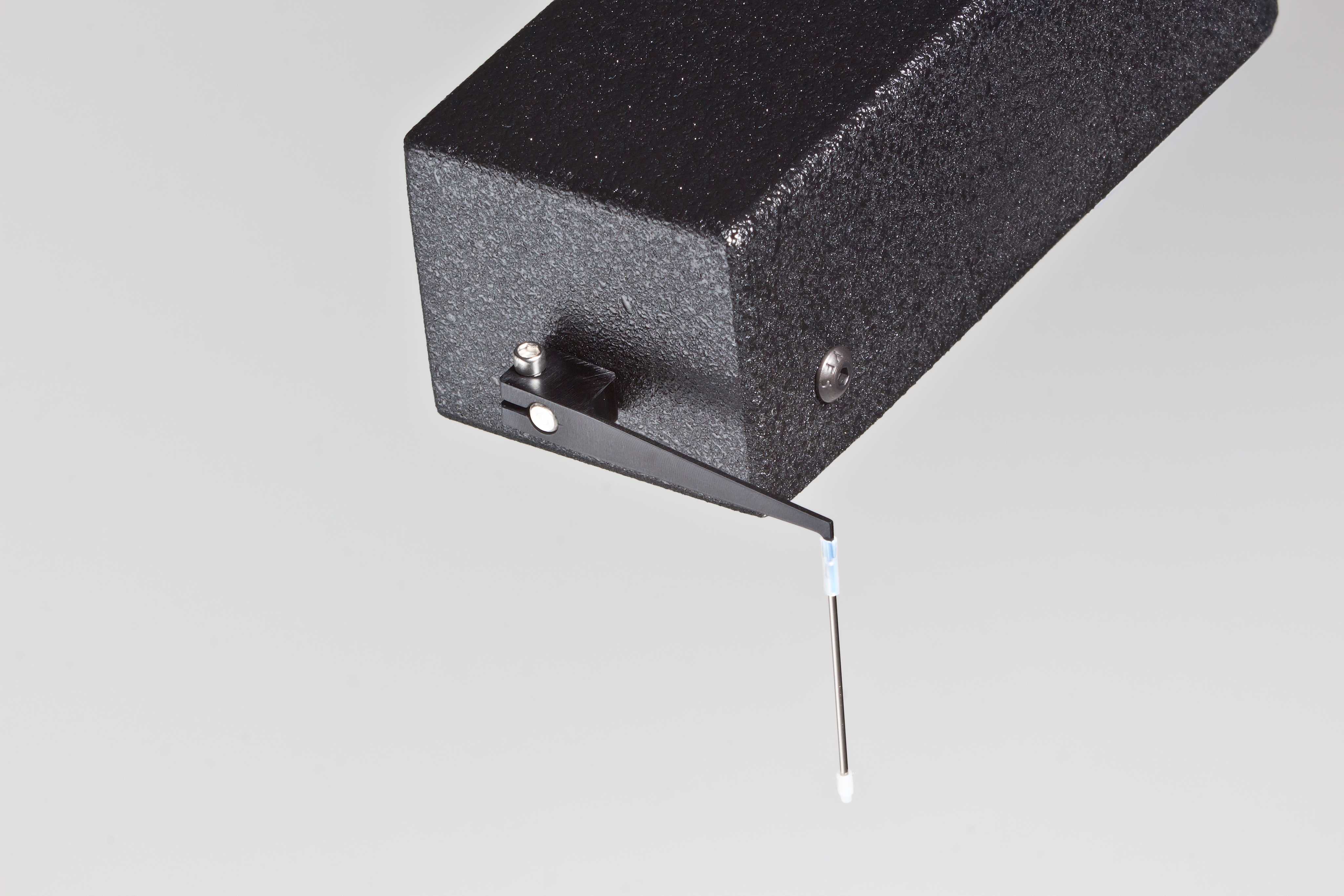
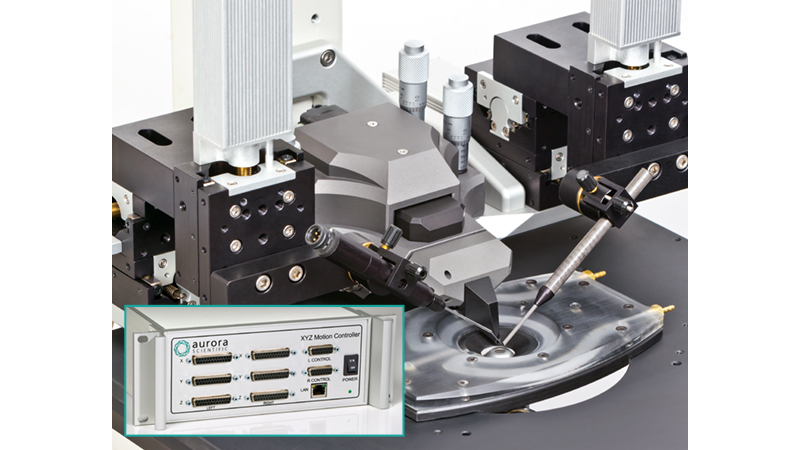
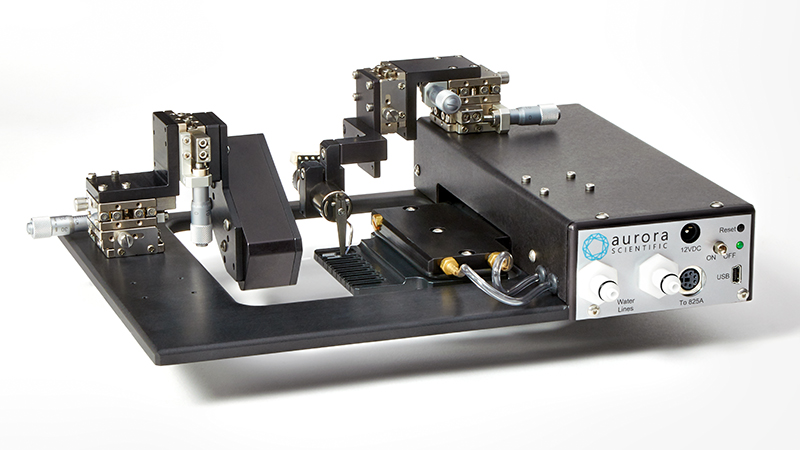
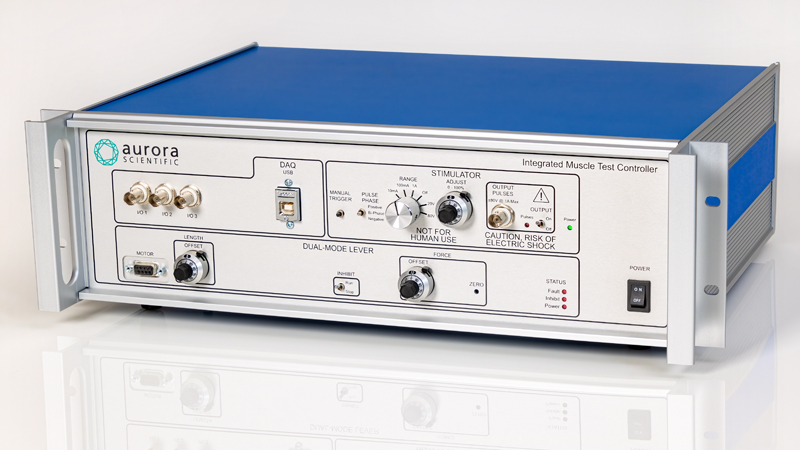
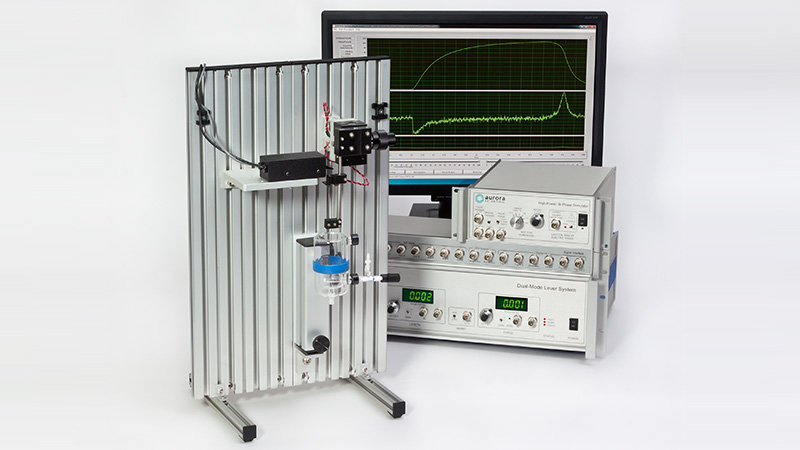
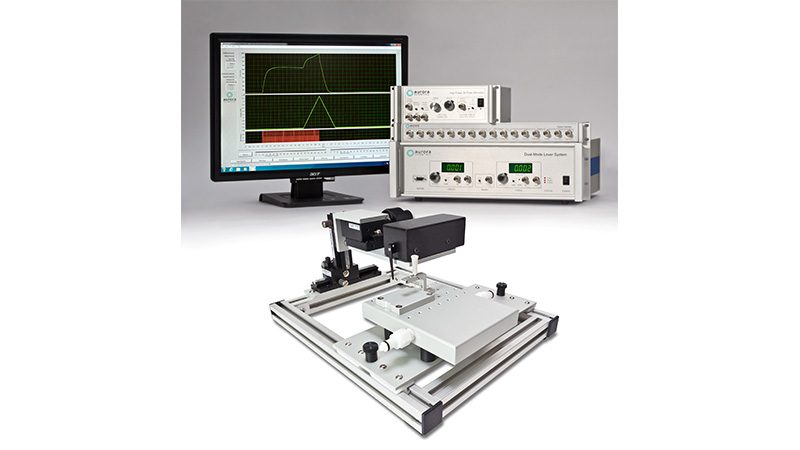
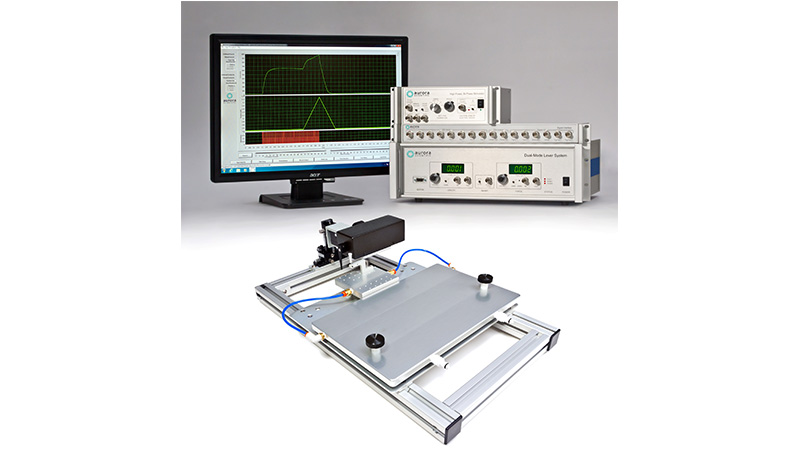
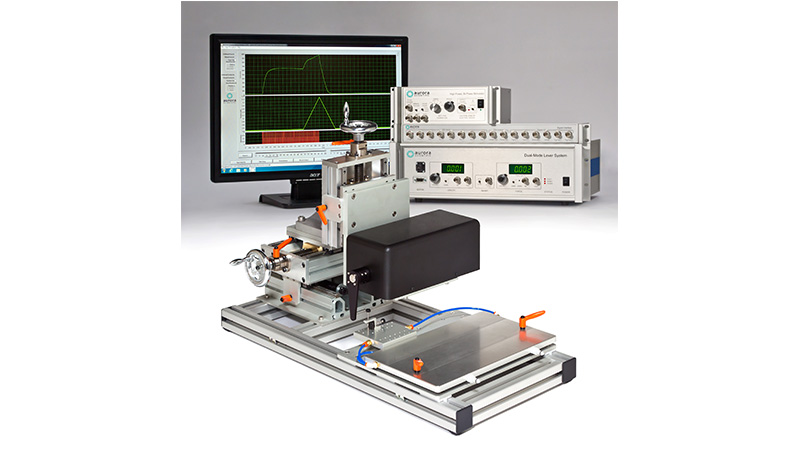
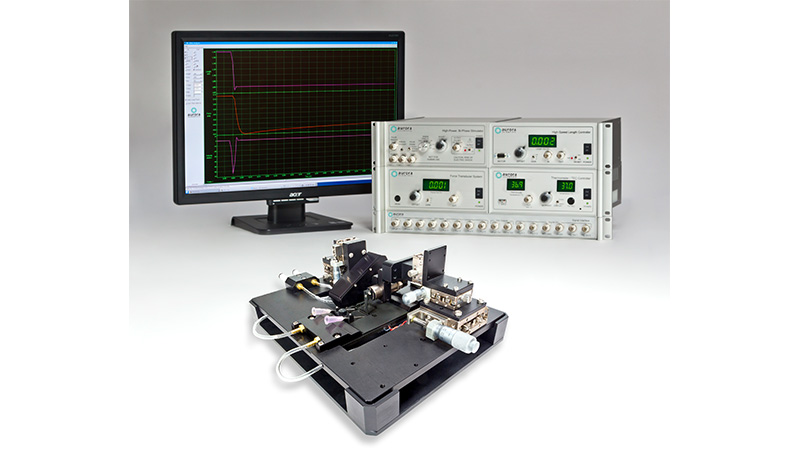
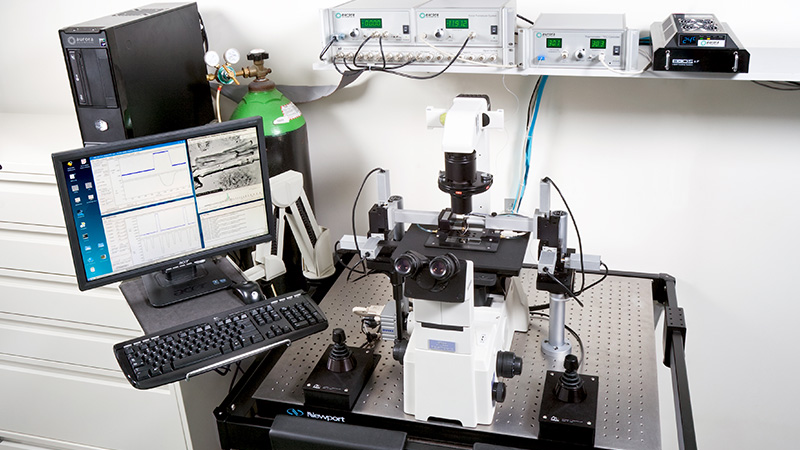
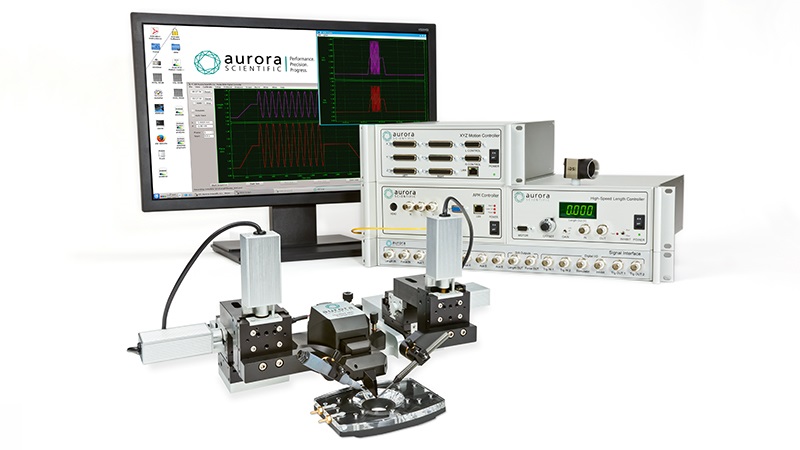
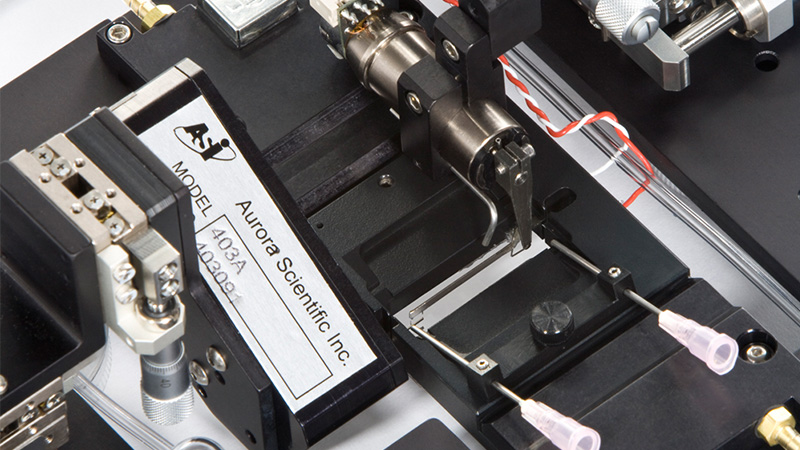
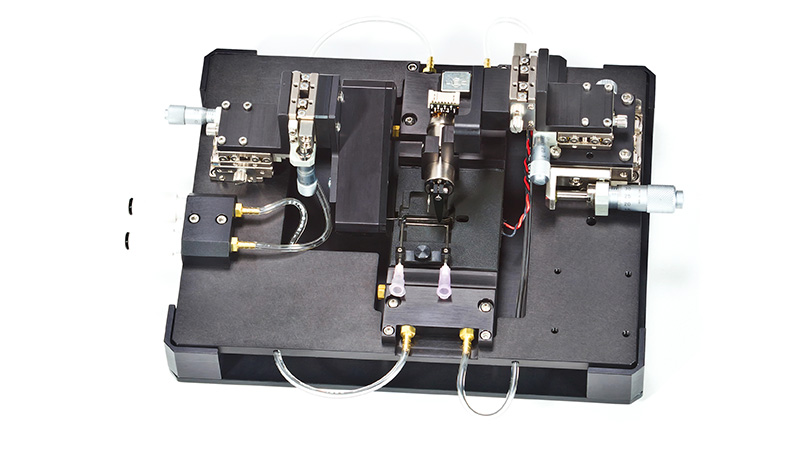
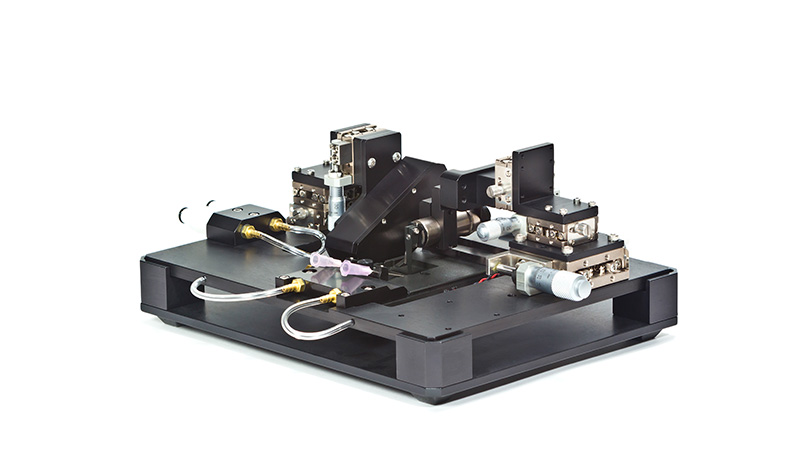
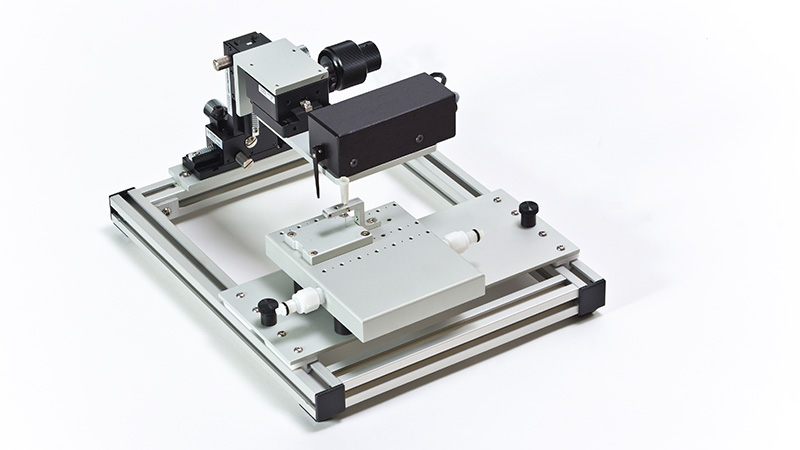
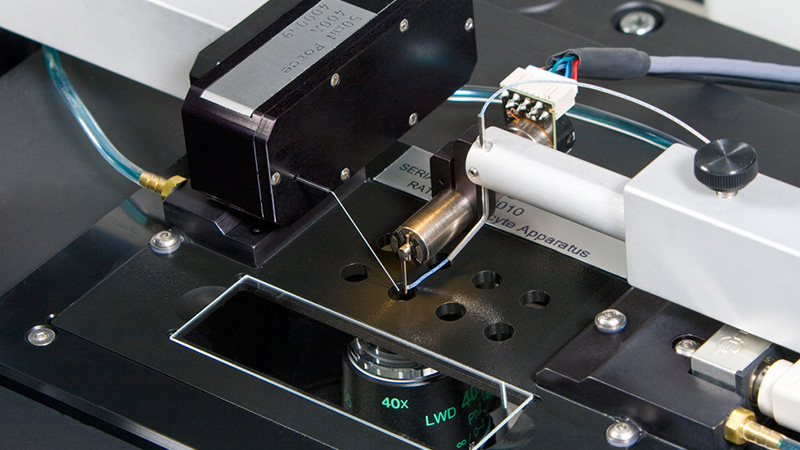
801C: 小型完整肌肉装置
801C小型完整肌肉测试仪器为生理学研究人员提供了一种测量小型组织肌肉力学的简单方法。新颖的试验室设计具有玻璃底部,集成了刺激电极和灌注,允许在保持组织活力的同时对样品进行成像。敞开式的水平设计也允许将密封盖子安装在原位,用于耗氧或缺氧研究。
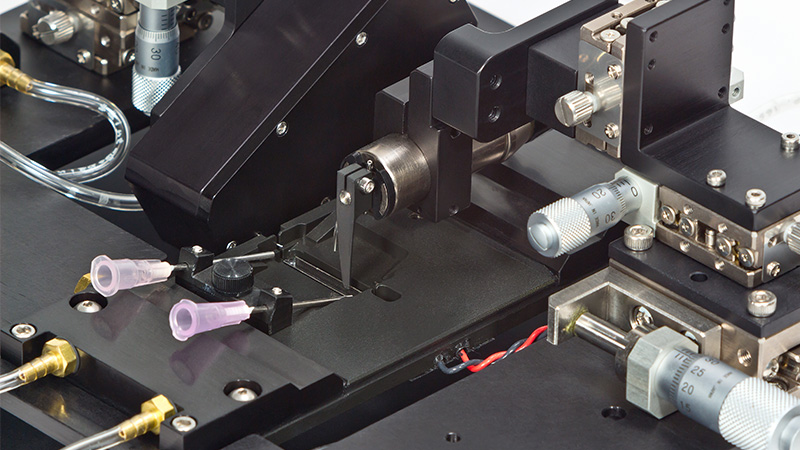
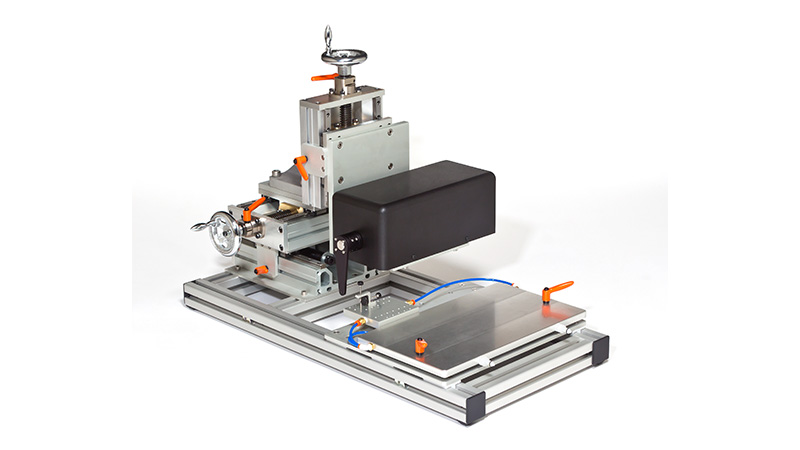
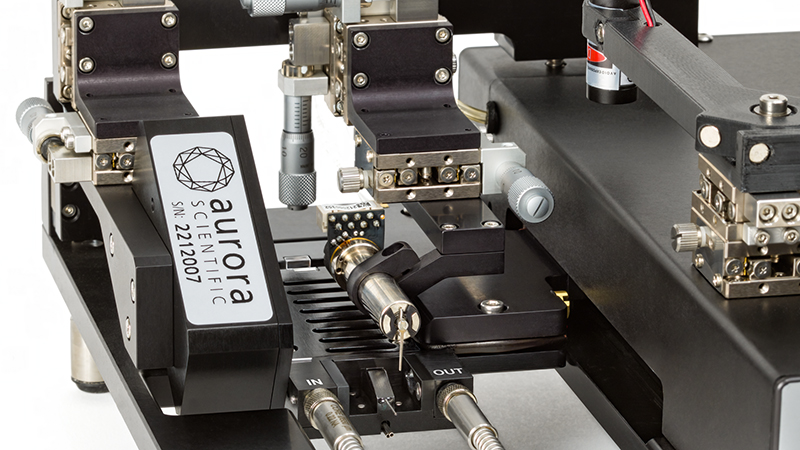
该设备包括一个Aurora Scientific高速长度控制器(322C)和一个精密力传感器(400A系列)的支架。各种尺寸的浴槽和浴槽配置可供选择,这为研究人员寻求研究不同的肌肉或组织单元和样品提供了理想的解决方案。从组织结构到斑马鱼,801C是功能性肌肉测量的严肃选择。
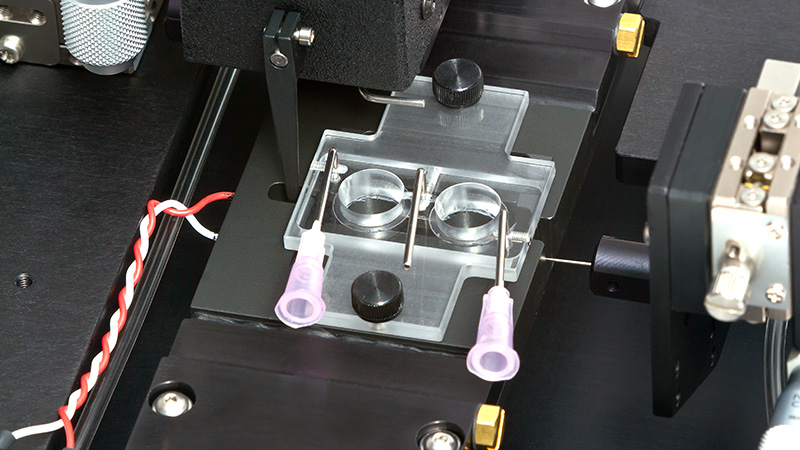
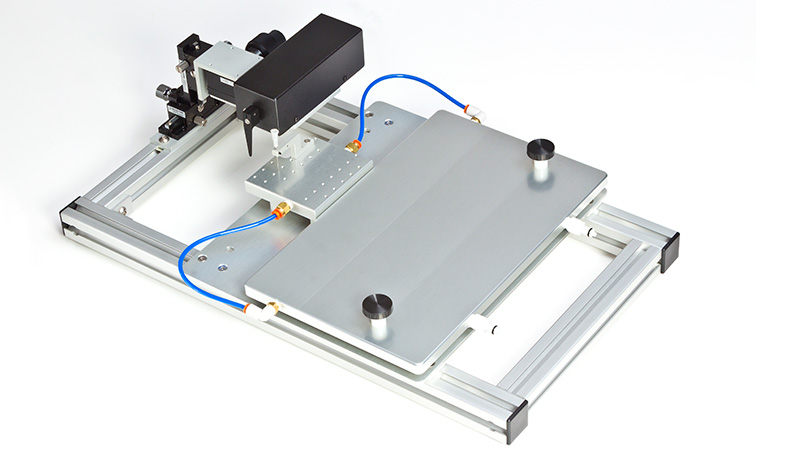
力传感器通过浴槽末端的一个独特的槽连接到肌肉上。这为人工肌肉构建或耗氧量研究提供了一个理想的配置,这些研究需要用一个可用的盖子将腔室密封。浴槽为流畅的灌注液流动进行了优化,包括浴槽两侧的溢出区,以提供接触组织的良好机会,同时最大限度地减少浴槽溢出的机会。
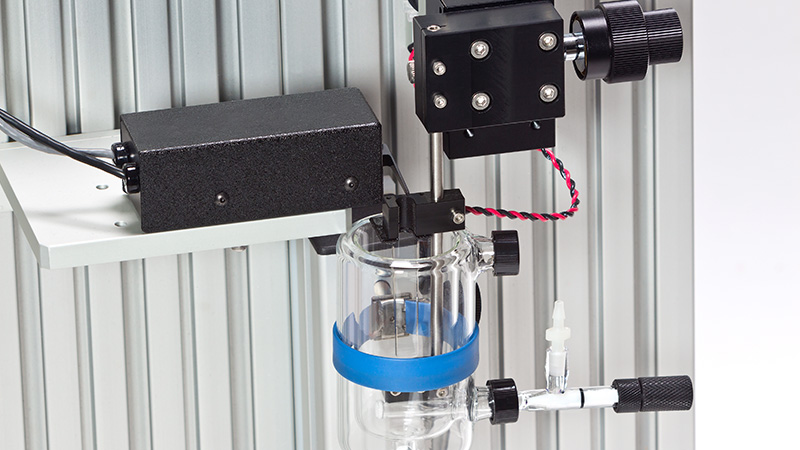
使用所提供的Aurora Scientific 825A热电控制器,试验板的温度可以控制在4至40°C之间,范围在+/-0.1°C。825A还包含一个低噪音的热电偶温度计,具有数字读数和电压输出。还包括一个Aurora Scientific 826A型水循环器。
● 为单一纤维、纤维束、纤维条和小块整肌设计
● 使用珀尔帖模块控制温度0-40°C
● 灌注池,有两种尺寸可供选择,400uL或1900uL
● XYZ测微仪,用于长度控制器和力传感器的控制。
● 包括用于灌注液的温度夹套式1升水箱。储液器包括氧气鼓泡器
● 包括铂金刺激电极
● 可与标准和倒置的显微镜一起使用
825A热电偶表/TEC控制器。
温度计和TEC控制器控制浴槽温度从0到40℃。
826A 水循环器。
水循环器为801C, 802D, 803B仪器提供冷却。包括水箱、泵和带风扇的散热器。
801-RES水箱组件。
1L热护套水箱,带增氧鼓泡器
Norden, Diana M. et al “Tumor growth increases neuroinflammation, fatigue and depressive-like behavior prior to alterations in muscle function.” Brain, Behavior, and Immunity (2015) DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.07.013
-
Tangney, Jared R. et al. “Timing and magnitude of systolic stretch affect myofilament activation and mechanical work.” American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology (2014) DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00233.2014
-
Raval, Kunil K. et al. “Pompe disease results in a Golgi-based glycosylation deficit in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.” The Journal of Biological Chemistry (2015) DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.628628
-
Heden et al. “Mitochondrial PE potentiates respiratory enzymes to amplify skeletal muscle aerobic capacity” Science Advances (2019) DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aax8352
-
Gharanei, Mayel “Investigation into the cardiotoxic effects of doxorubicin on contractile function and the protection afforded by cyclosporin A using the work-loop assay.” Toxicology in Vitro (2014) DOI: 10.1016/j.tiv.2014.01.011
-
Munarin et al. “Engineered human myocardium with local release of angiogenic proteins improves vascularization and cardiac function in injured rat hearts” Biomaterials (2020) DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120033
-
de Lange, Willem J. et al. “E258K HCM-causing mutation in cardiac MyBP-C reduces contractile force and accelerates twitch kinetics by disrupting the cMyBP-C and myosin S2 interaction.” The Journal of General Physiology (2013) DOI: 10.1085/jgp.201311018
-
Gharanei, Mayel et al. “Doxorubicin induced myocardial injury is exacerbated following ischaemic stress via opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore.” Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology (2013) DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2012.12.003
-
Dwenger et al. “Chronic Optogenetic Pacing of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Engineered Cardiac Tissues” Channelrhodopsin (2020) DOI: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0830-2_10
-
de Lange, Willem J. et al “Ablation of cardiac myosin-binding protein-C accelerates contractile kinetics in engineered cardiac tissue.” Journal of General Physiology (2013) DOI: 10.1085/jgp.201210837
-